Cybernetics and Generic System Modeling
Some Streams of Systemic Thought
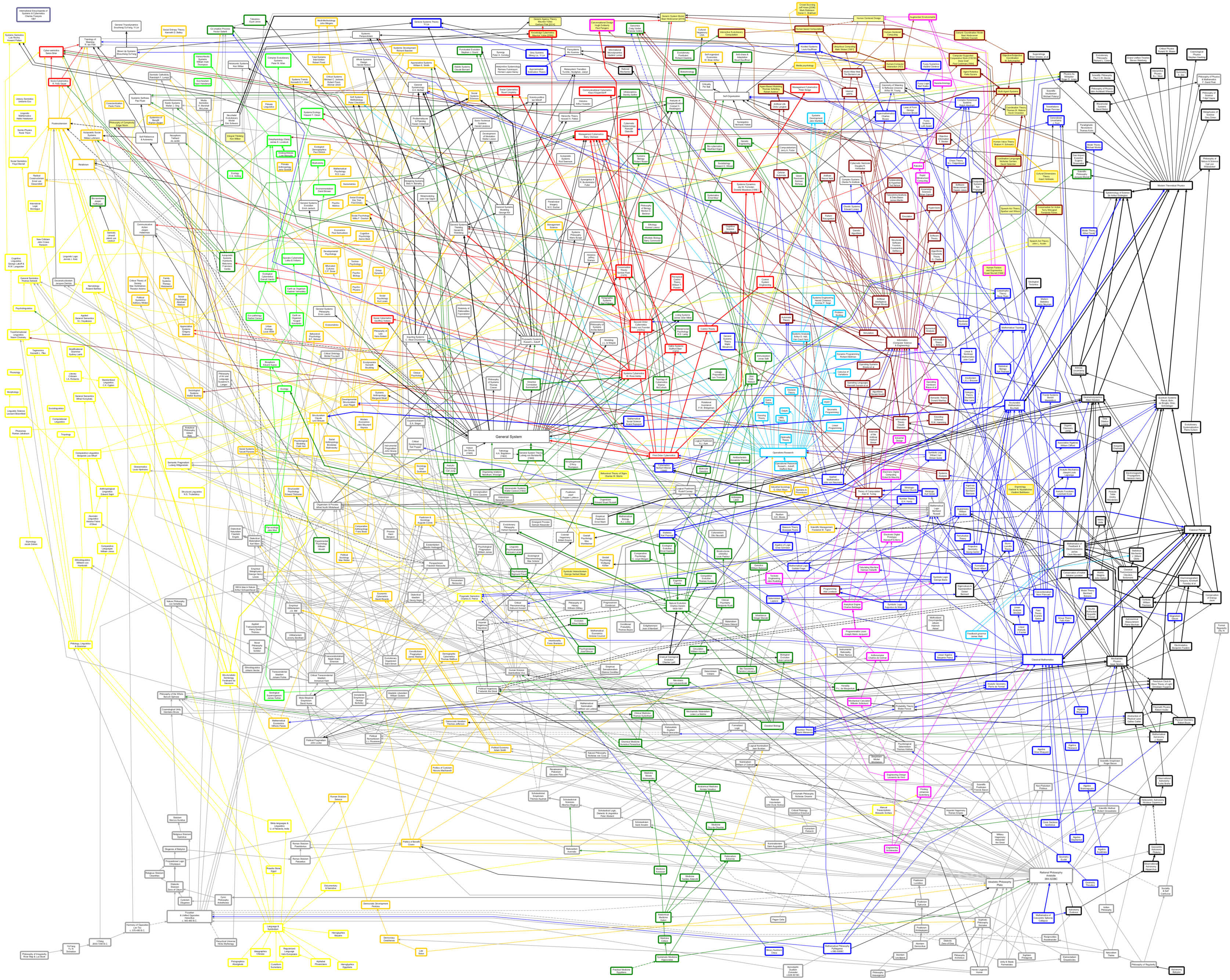
In terms of systems thinking, an extensive map of related work and their influences is presented by the International Institute for General Systems Studies (IIGSS, 2001). This map was originated by E. Schwarz in 1996. It includes the influences of researchers in the domains of mathematics, physics, computer science, engineering, cybernetics, systemics, biology, ecology, sociology and philosophy fromancient times to the present.
With the permission of Jeffrey Yi-Lin Forrest (director of IIGSS), we update the map and add recent work in the field of cybernetics, systemics and coordination. Because the latest source files of that map are missing, we completely redraw it. We choose graphml, an open source format for graph design.
Legend of Map
The map encompasses different nodes and edges. The nodes denote topics, such as scientific work or research areas. Major influences between the topics are illustrated by directed edges. The map uses a color-code to show the major scientific realm of nodes and edges:
- white: general system
- red: cybernetics
- black: physical sciences
- blue: mathematics
- dark red: computers & informatics
- green: biology & medicine
- yellow: symbolic systems
- orange: social systems
- light green: ecology
- gray: philosophy
- cyan: systems analysis
- purple: engineering
History
- Originated in 1996 by Dr. Eric Schwarz, Neuchâtel, Switzerland.
- Extended in 1998, including items from the "The Story of Philosophy" by Will Durant (1933).
- Elaborated in 2000-2001 from many sources for the International Institute for General Systems Studies.
- Extended in 2016 by Benjamin Hadorn, Fribourg, Switzerland.
Your contribution: Feel free to extend and correct the graph. Please send an updated version to us in order to keep a current version online.
Thanks.